Barcodes are integral to modern logistics, retail, and even personal management, providing a quick way to access data.
You will be surprised when you read your barcode and get the data quickly.
Also, with a smartphone, anyone can transform their device into a barcode scanner, unlocking information effortlessly.
This post will show you how to read barcodes seamlessly. Let’s start!
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form.
Originally, barcodes systematically represented data by varying the widths and spacings of parallel lines, which may be referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D).
Today, they also come in patterns of squares, dots, hexagons, and other two-dimensional (2D) forms, like QR codes.

Barcodes are widely used for multiple purposes, including tracking items in retail settings, managing warehouse inventory, and automating checkout processes in supermarkets.
Each barcode contains unique data, which typically represents something about the item it’s attached to, such as its manufacturer, product type, and unique item number.
This system of tagging and identification enhances the speed and accuracy of data handling and retrieval in various systems.
Understanding the Structure of a Barcode
The structure of a typical linear barcode includes several components:
- Quiet Zone: This is the blank margin on either end of a barcode that tells the barcode reader where the barcode starts and ends.
- Start and Stop Characters: These special bar patterns indicate the barcode's beginning and end to the scanner.
- Data Characters: These are the bars and spaces in the middle of the barcode that encode the actual information. Each character is made up of a series of bars and spaces of varying widths.
- Check Digit: This is a calculated number used to verify the accuracy of the entire barcode. It helps ensure that the barcode is scanned correctly and reduces the possibility of errors.
The structure of 2D barcodes, like QR codes, is more complex, allowing them to hold more information. These barcodes consist of black-and-white pixel patterns that can encode a variety of data types, such as numeric, alphanumeric, byte/binary, and even Kanji symbols. The arrangement includes:
- Finder Patterns: These are typically located at three corners of the QR code to help the scanner identify and orient the code correctly.
- Timing Patterns: These help scanners determine the size of each data cell.
- Data Cells: These contain the actual data being encoded.
- Error Correction Code (ECC): This helps restore the data if the code is dirty or damaged.
Both types of barcodes are crucial in modern commerce and logistics, streamlining processes and reducing human error.
Different Types of Barcodes
Barcodes come in various formats, each designed for specific uses based on the amount and type of data they can carry and the environment in which they are used.
Here’s an overview of some of the different types of barcodes:
1. Linear (1D) Barcodes

- UPC (Universal Product Codes): Used widely in retail, particularly in the United States and Canada, for tracking trade items in stores.
- EAN (European Article Number): Similar to UPC, but used more commonly internationally. There are two main types, EAN-13 and EAN-8, the latter being a compressed version used for smaller items.
- Code 128: Highly versatile and can encode all 128 characters of the ASCII set. It’s used for logistics and transportation labels.
- Code 39: Can encode letters and numbers, making it a popular choice for various industries, including automotive and defense.
- Interleaved 2 of 5: A numeric-only barcode used primarily for warehouse, distribution, and manufacturing environments.
2. Two-Dimensional (2D) Barcodes

- QR Code: Quick Response codes can hold a significant amount of data, including URL links, texts, and more. They can be read by smartphones, making them popular for marketing and consumer applications.
- Data Matrix: Often used in electronics manufacturing for marking small items, given its ability to encode a lot of data in a small space.
- PDF417: A stacked linear barcode that can hold large amounts of data, including photographs and fingerprints. It’s used in government IDs and postal services.
3. Composite Barcodes

- Composite Codes: These combine a 2D barcode stacked atop a linear barcode, allowing both to be scanned together. They are used in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries to add extra data without needing more label space.
4. Postal Barcodes

- IM (Intelligent Mail) Barcode: Used by postal services to increase the speed, quality, and accuracy of mail delivery.
- POSTNET: Used by the U.S. Postal Service for automating the sorting and delivery of mail.
Each type of barcode has its own specific structure, character set, and field of application, and it is designed to meet different technical and business needs.
How to Read a Barcode with QRCodeDynamic
Step 1- Go to QRCodeDynamic’s Barcode Reader.
Here is the link to Barcode Reader: https://qrcodedynamic.com/barcode-reader
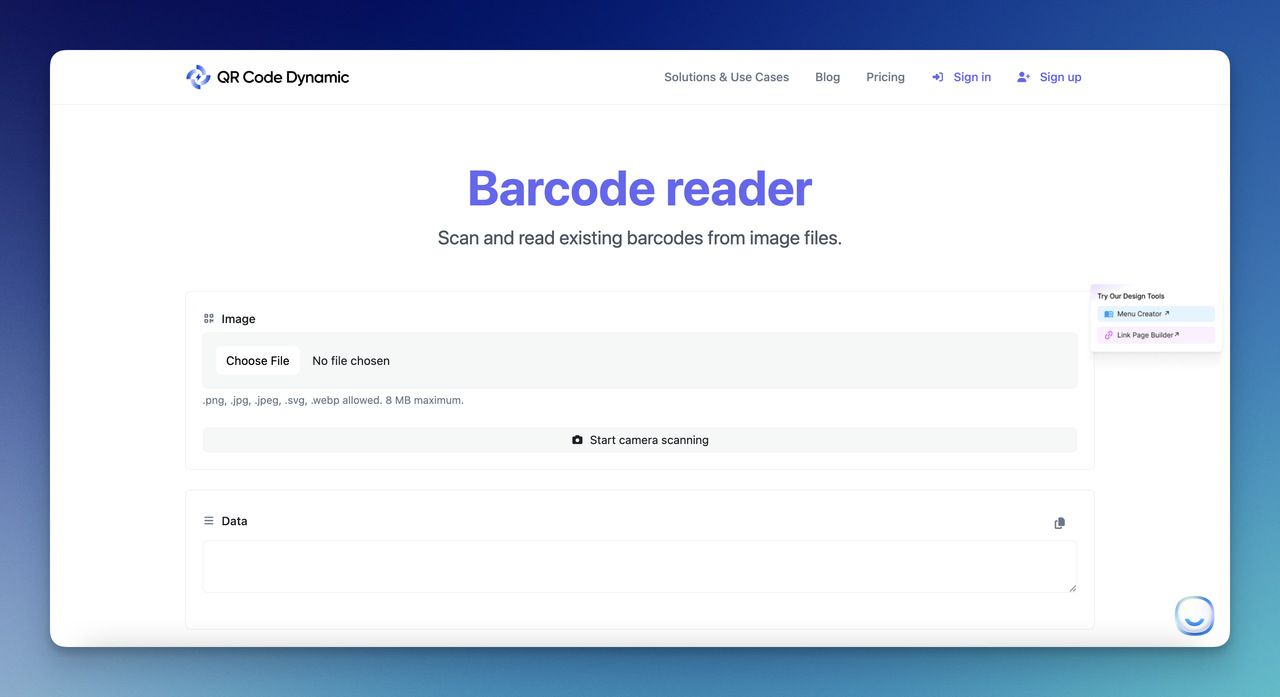
Step 2- Choose your scanning option.
There are two options here: from the image and from the camera.
The Image part includes different image formats, like .png, .jpg, .jpeg, .svg, .webp.
Plus, you can upload images by choosing a file up to 8 MB.
The Camera part works effectively if you have the barcode with you. You can easily get the data.
If you scan the barcode on your phone, there are various possibilities for changing the camera.
- Front Camera
- Back dual wide camera
- Back ultra wide camera
- Back camera
You can stop the camera whenever you want.
Step 3- Copy the data from the content box to use later.
And that’s how it is easy to scan your barcodes with QRCodeDynamic.
How to Read Barcode on Your Phone
Reading barcodes using your smartphone is a convenient way to access product information, track inventory, or even redeem coupons.
The process is straightforward whether you are using an iPhone or an Android device. Here’s how you can do it:
Step 1: Choose the Right App
- For iOS Users: The Camera app on iPhones can natively scan QR codes. For other barcode types, you might need a dedicated app such as "Barcode Scanner" or "Quick Scan."
- For Android Users: Some Android phones have built-in QR code scanners that are accessible via the Camera app or Google Lens. For more comprehensive barcode scanning, apps like "Barcode Scanner" or "QR & Barcode Reader" are recommended.
Step 2: Install the App
- Download and install your chosen barcode scanning app from the App Store (iOS) or Google Play Store (Android). Read the reviews and check the ratings to ensure the app is reliable and secure.
Step 3: Open the App
- Launch the app on your smartphone. Most barcode-scanning apps will request permission to access your camera. Grant this permission so the app can use the camera to scan barcodes.
Step 4: Scan the Barcode
- Position the Barcode: Hold your phone so the camera is directly above the barcode. Ensure the entire barcode is within the camera’s viewfinder.
- Adjust the Distance: Move your phone closer or farther away until the app recognizes the barcode and captures it. This usually involves aligning the barcode with a specific on-screen guide or box.
- Scan in Good Lighting: Ensure there is adequate lighting. If the barcode isn’t scanning, try increasing the light level or moving to a location with better lighting.
Step 5: View the Information
- Once the barcode is scanned, the app will decode it and display the relevant information on your screen. This could be product details, a website link, nutritional information, or inventory data, depending on the barcode type and the app’s functionality.
Step 6: Take Action
- Depending on what the barcode contains, you might have options to take further actions. For example, if it’s a product link, you can visit the website; if it’s a coupon, you can save it; or if it’s inventory data, you can update records.
Simple Keys for Better Scanning
- Steady Your Hand: A steady hand helps prevent blurry scans.
- Use Horizontal Orientation: Some barcodes scan better when the phone is held horizontally.
- Clean Your Camera Lens: A clean lens gives clearer scans.
By following these steps, you can effectively use your smartphone as a barcode scanner, making it a versatile tool for a variety of practical applications.
Tips for Accurate Barcode Reading
Accurate barcode reading is crucial for efficiency in retail, logistics, and inventory management. As an expert in barcode reading, I recommend the following practices to ensure reliable scans and minimize errors:
1. Ensure Proper Barcode Quality

- Print Quality: Make sure that barcodes are printed clearly. Poor print quality can lead to smudges or faded bars, which are difficult for scanners to read. Use high-quality printers and check the print resolution to ensure clarity.
- Barcode Size: Adhere to the recommended size for your specific barcode type. If a barcode is too small, scanners might have difficulty reading it, and if too large, it might not be read correctly at close range.
- Contrast: Ensure good contrast between the barcode and its background (usually black bars on a white background) to maximize readability.
2. Use the Right Scanner
- Type of Scanner: Choose a scanner that matches the type of barcode you are using. For instance, laser scanners are great for 1D barcodes, whereas 2D barcodes typically require an imager scanner.
- Configuration: Regularly update your scanner’s software and configure settings according to the barcode type and intended use. Proper configuration can significantly improve scanning accuracy.
3. Optimal Scanner Handling
- Proper Alignment: Hold the scanner at the correct angle and distance from the barcode. Each scanner type has a specific optimal scanning distance and angle; refer to the scanner’s manual for guidance.
- Steady Handling: Keep the scanner steady during scanning. Movement can blur the scan, making it harder for the device to interpret the barcode.
4. Regular Maintenance

- Clean Your Scanners: Keep the scanner lens clean from dust and smudges, which can interfere with its ability to read barcodes.
- Inspect Scanners Regularly: Check for signs of wear or damage, particularly on portable or handheld units. Replace faulty scanners immediately to avoid errors.
5. Environmental Considerations
- Lighting Conditions: Ensure sufficient lighting for scanning. Some barcodes may reflect too much light or become unreadable under certain artificial lights.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight: Direct sunlight can cause glare on barcode labels, making them difficult to scan. Position barcodes away from direct sunlight when possible.
6. Test and Validate
- Routine Testing: Regularly test barcodes with your scanners to ensure they read correctly every time. This is especially important when introducing new types of barcodes or scanners into your operations.
- Error Checking: Implement systems that check for scanning errors and alert operators immediately. This allows for quick corrections and reduces the chance of data errors.
By following these expert tips, you can optimize your barcode system for quick and accurate data capture, which is essential for maintaining efficiency and accuracy in any operation reliant on barcode technology.
Conclusion
Learning barcode scanning can enhance many aspects of daily life, from shopping and price comparisons to inventory management.
With this skill, you harness the power of quick, accurate data access right in your pocket, streamlining tasks and uncovering hidden details in everyday objects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why can't I read a barcode with the human eye?
Barcodes are designed to be read by machines, not the human eye. The lines and spaces in a barcode correspond to numerical codes that a machine can decipher but are difficult for a human to interpret.
Can a barcode be explained manually?
Yes, a barcode can theoretically be decoded manually, but it would involve understanding the specific symbology of the barcode type, which can be complex and time-consuming.
Are barcodes unique to each product?
Yes, barcodes, specifically UPCs and EANs, are unique for each individual product variant. For example, the same product in different sizes or colors would each have different barcodes.
Can a barcode be damaged and still readable?
It is possible for a barcode to be read even if it is slightly damaged, depending on the severity of the damage. However, if a significant portion of the barcode is damaged or obscured, it may become unreadable.
Discover our other blog posts:


